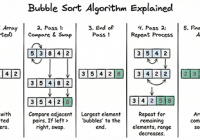
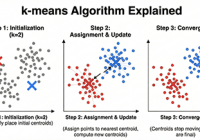
Euclidean Algorithm
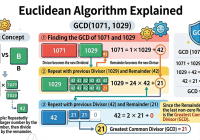
simple algorithm The Euclidean algorithm is a classical method for computing the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two non‑negative integers.The key idea is based on the following property: For any integers a and b (with a ≥ b), the GCD of a and b is the same as the GCD of b and a mod b. Because the remainder becomes strictly smaller each step, the process terminates after only a few iterations, even… Read More »