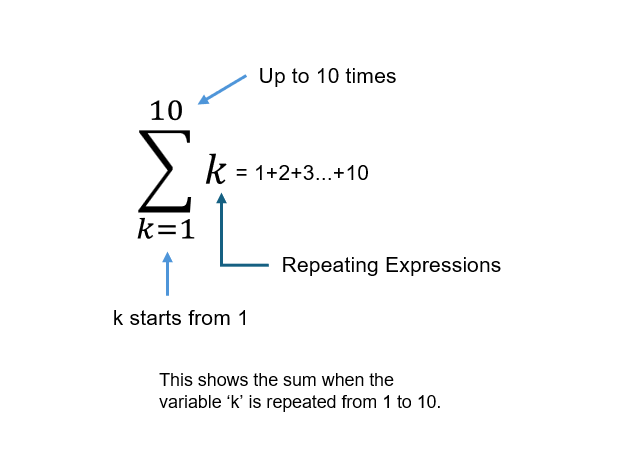
Calculate the Σ symbol expression that represents the sum of natural numbers using NumPy.
What is NumPy?
NumPy is a Python library for numerical computation. It’s particularly strong in array operations (vectors and matrices) and allows for fast calculations. We can efficiently perform calculations like summing natural numbers.
import numpy as np
# Create an array of integers from 1 to 10
numbers = np.arange(1, 11) # arange creates an array with integers spaced evenly within a specified range
# Calculate the sum of the elements in the array
total_sum = np.sum(numbers)
# Display the result
print("Sum of natural numbers from 1 to 10:", total_sum)
Code Explanation
import numpy as np: Imports the NumPy library. We use the aliasnpto easily call NumPy functions.numbers = np.arange(1, 11): Uses thenp.arange()function to create an array containing integers from 1 to 10.- It’s specified in the format
arange(start_value, end_value). - The end value is not included, so we specify 11 to create an array from 1 to 10.
- It’s specified in the format
total_sum = np.sum(numbers): Uses thenp.sum()function to calculate the sum of all elements in thenumbersarray.print("Sum of natural numbers from 1 to 10:", total_sum): Displays the calculated result on the screen.
Why isn’t the end value included?
There are several reasons for this design:
- Half-Open Interval: In mathematical convention, intervals are often represented as “(start_value, end_value),” including the start value but excluding the end value.
np.arange()follows this half-open interval concept. - Intuitive Usability: For example, if you want to generate numbers from 0 to 9, you can easily create the desired array by writing
np.arange(0, 10). Not including the end value allows for this intuitive description.