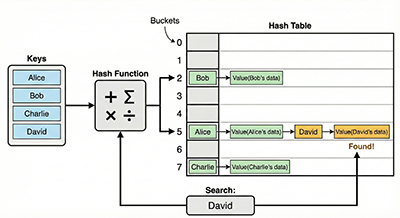
Hash table search is an algorithm for efficiently searching data. Instead of looking sequentially like in a regular array, it uses a “hash function” to convert the data into an “index” where the data is stored, enabling fast access.
Imagine:
Let’s consider finding a book in a library.
- Normal Search: Looking at every shelf one by one (takes time).
- Hash Table Search: Calculating a specific number from the book title and looking only on that numbered shelf (faster to find).
How Hash Table Search Works
- Hash Function: A function that takes data you want to search for (e.g., an employee ID) as input and returns an integer value within the range of 0 to N-1. This value becomes the index where the data is stored.
- Hash Table: Prepare a pre-defined size array called a hash table.
- Data Storage: Store the data at the location corresponding to the index calculated by the hash function.
- Data Search: Apply the hash function to the data you want to search for, and refer to the data located at the same index.
class HashTable:
def __init__(self, size):
self.size = size
self.table = [None] * size # Initialize the hash table
def hash_function(self, key):
"""Hash function: Converts a key to an index"""
return key % self.size
def insert(self, key, value):
"""Insert data"""
index = self.hash_function(key)
self.table[index] = (key, value) # Store the key and value as a pair
def search(self, key):
"""Search for data"""
index = self.hash_function(key)
if self.table[index] is not None and self.table[index][0] == key:
return self.table[index][1] # Return the value
else:
return None # Return None if not found
def delete(self, key):
"""Delete data"""
index = self.hash_function(key)
if self.table[index] is not None and self.table[index][0] == key:
self.table[index] = None # Empty the storage location
# Example Usage
hash_table = HashTable(10)
hash_table.insert(5, "apple")
hash_table.insert(25, "banana")
hash_table.insert(15, "orange")
print(hash_table.search(5)) # apple
print(hash_table.search(25)) # banana
print(hash_table.search(30)) # None
hash_table.delete(5)
print(hash_table.search(5)) # None
Code Explanation
- The
HashTableclass manages the hash table. hash_functiontakes a key (e.g., an employee ID) as input and calculates the index of the hash table. Here, it simply calculateskey % size, but more complex functions can also be used.insertstores the key and value in the hash table.searchsearches for a value corresponding to the key.deletedeletes data corresponding to the key.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Hash Table Search
Advantages:
- Fast Search: Can search in O(1) on average (ideal case).
- Fast Data Storage and Deletion: Also O(1) on average.
Disadvantages:
- Collision: Different keys may hash to the same index, causing a “collision”.
- Measures to resolve collisions are necessary (see below).
- Hash Function Design is Important: A poor hash function can lead to many collisions and reduced performance.
- Memory Usage: May waste memory depending on the size of the hash table.
Summary
Hash table search is a powerful algorithm for achieving fast data retrieval. However, collision handling and hash function design are important considerations.