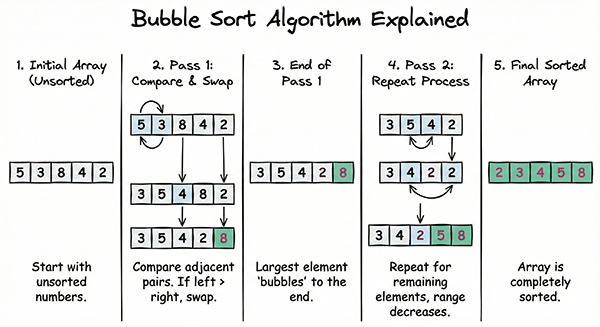
Bubble sort is one of the simplest sorting algorithms. It works by repeatedly stepping through the list, comparing adjacent elements and swapping them if they are in the wrong order. Larger elements “bubble” to the end of the list with each pass. This process continues until the entire list is sorted in ascending (or descending) order.
Example:
Let’s consider sorting the following list in ascending order:
[5, 1, 4, 2, 8]
- First Pass:
- Compare (5, 1) → Swap →
[1, 5, 4, 2, 8] - Compare (5, 4) → Swap →
[1, 4, 5, 2, 8] - Compare (5, 2) → Swap →
[1, 4, 2, 5, 8] - Compare (5, 8) → No swap →
[1, 4, 2, 5, 8](The largest value, 8, moves to the end)
- Compare (5, 1) → Swap →
- Second Pass:
- Compare (1, 4) → No swap →
[1, 4, 2, 5, 8] - Compare (4, 2) → Swap →
[1, 2, 4, 5, 8] - Compare (4, 5) → No swap →
[1, 2, 4, 5, 8](The second largest value, 5, moves to the second-to-last position)
- Compare (1, 4) → No swap →
- Third Pass:
- Compare (1, 2) → No swap →
[1, 2, 4, 5, 8] - Compare (2, 4) → No swap →
[1, 2, 4, 5, 8]
- Compare (1, 2) → No swap →
- Fourth Pass:
- Compare (1, 2) → No swap →
[1, 2, 4, 5, 8]
- Compare (1, 2) → No swap →
The list is now sorted, so the sorting process is complete.
def bubble_sort(list_):
"""
Sorts a list in ascending order using bubble sort.
Args:
list_: The list to be sorted.
Returns:
The sorted list.
"""
n = len(list_)
for i in range(n - 1): # Number of passes (n-1) times
for j in range(n - i - 1): # Number of comparisons in each pass
if list_[j] > list_[j + 1]:
# Swap adjacent elements
list_[j], list_[j + 1] = list_[j + 1], list_[j]
return list_
# Example Usage
my_list = [5, 1, 4, 2, 8]
sorted_list = bubble_sort(my_list)
print("Sorted list:", sorted_list) # Output: Sorted list: [1, 2, 4, 5, 8]
Characteristics of Bubble Sort:
- Time Complexity: O(n^2) in the worst and average cases. This means that the processing time increases significantly as the number of elements grows.
- Space Complexity: O(1). It uses very little extra memory (in-place sort).
- Stable Sort: Maintains the relative order of equal elements.
Bubble sort is easy to implement, but it’s inefficient for sorting large lists. It’s recommended to use faster algorithms like merge sort or quicksort for larger datasets.