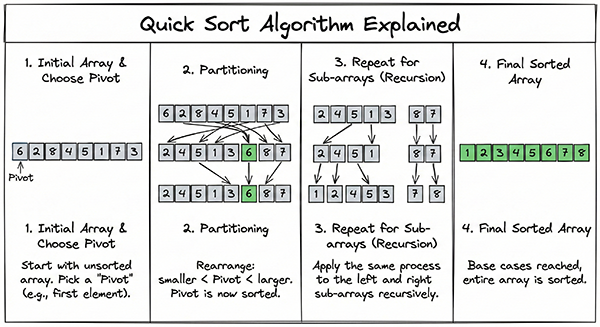
Quicksort is an efficient sorting algorithm based on the divide-and-conquer paradigm. It works as follows:
- Pivot Selection: Choose one element from the array to be sorted. This element is called the “pivot.”
- Partitioning: Divide the array into two groups: elements smaller than the pivot and elements larger than the pivot. The pivot is placed in its correct position (usually a sorted position).
- Recursive Sorting: Recursively apply steps 1 and 2 to each of the divided groups.
- Combining: Once the recursive calls are complete, the groups are already sorted, so simply combining them sorts the entire array.
Example of Quicksort:
Let’s consider sorting the following array [5, 2, 8, 1, 9, 4, 7].
- Pivot Selection: Choose the first element
5as the pivot. - Partitioning:
- Elements smaller than
5:[2, 1, 4] - Elements larger than
5:[8, 9, 7] - Pivot:
5At this point, the array looks like[2, 1, 4, 5, 8, 9, 7].
- Elements smaller than
- Recursive Sorting:
- Apply quicksort to
[2, 1, 4].- Pivot:
2 - Partition:
[1], [4], 2->[1, 2, 4]
- Pivot:
- Apply quicksort to
[8, 9, 7].- Pivot:
8 - Partition:
[7], [9], 8->[7, 8, 9]
- Pivot:
- Apply quicksort to
- Combining: Combining
[1, 2, 4],5, and[7, 8, 9]results in the sorted array[1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9].
Python Code Example
def quicksort(arr):
"""
Sorts an array using Quicksort.
Args:
arr: The array to be sorted.
Returns:
The sorted array.
"""
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr # Array is already sorted if empty or has one element
pivot = arr[0] # Choose the first element as the pivot
less = [i for i in arr[1:] if i <= pivot] # List of elements smaller than the pivot
greater = [i for i in arr[1:] if i > pivot] # List of elements larger than the pivot
return quicksort(less) + [pivot] + quicksort(greater)
# Example Usage
arr = [5, 2, 8, 1, 9, 4, 7]
sorted_arr = quicksort(arr)
print(f"Before sorting: {arr}")
print(f"After sorting: {sorted_arr}")
Quicksort Characteristics:
- Average Time Complexity: O(n log n) – Very fast algorithm.
- Worst-Case Time Complexity: O(n^2) – Performance can degrade depending on how the pivot is chosen.
- Space Complexity: O(log n) – Uses stack space for recursive calls (on average).
- In-place Sort: Requires minimal additional memory (although stack space for recursion is needed).
Pivot Selection Strategies:
The choice of pivot significantly impacts Quicksort’s performance.
- Choosing the First Element: The simplest method, but can lead to worst-case performance with already sorted arrays.
- Choosing Randomly: Choosing a random pivot helps avoid the worst case.
- Choosing the Median: Selecting the median as the pivot is expected to result in more balanced partitioning.
Quicksort is widely used due to its relatively simple implementation and speed. However, be mindful of the worst-case time complexity and consider appropriate pivot selection strategies.