The Levenshtein distance (also known as edit distance) is a metric for measuring the similarity between two strings. It’s defined as the minimum number of operations required to transform one string into the other using insertion, deletion, and substitution operations.
We can efficiently calculate the Levenshtein distance using dynamic programming.
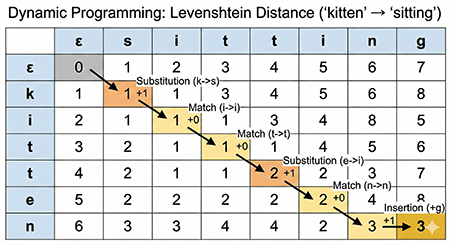
Example: Levenshtein Distance between “kitten” and “sitting”
Let’s consider two strings s1 = "kitten" and s2 = "sitting" as an example.
Here are the steps to count the number of operations:
- kitten → sitten (substitution: k → s)
- sitten → sittin (substitution: e → i)
- sittin → sitting (insertion: g)
In this case, the Levenshtein distance is 3.
Dynamic Programming Approach
Dynamic programming involves creating and filling in the following table:
dp[i][j] represents the Levenshtein distance between the first i characters of s1 and the first j characters of s2.
| s | i | t | t | i | n | g | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| k | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| i | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| t | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| t | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| e | 5 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| n | 6 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
How to fill in the table:
dp[0][j] = j: The distance between an empty string and the firstjcharacters ofs2is equal to the number of insertion operations, which isj.dp[i][0] = i: The distance between the firsticharacters ofs1and an empty string is equal to the number of deletion operations, which isi.dp[i][j]is the minimum of the following:dp[i-1][j] + 1: The cost of deleting thei-th character ofs1(deletion)dp[i][j-1] + 1: The cost of inserting thej-th character ofs2(insertion)dp[i-1][j-1] + (0 if s1[i-1] == s2[j-1] else 1): If thei-th character ofs1and thej-th character ofs2are equal, the cost is 0; otherwise, it’s the cost of substitution (1)
Finally, dp[len(s1)][len(s2)] is the Levenshtein distance.
def levenshtein_distance(s1, s2):
"""
Calculates the Levenshtein distance using dynamic programming.
Args:
s1 (str): The first string.
s2 (str): The second string.
Returns:
int: The Levenshtein distance.
"""
len_s1 = len(s1)
len_s2 = len(s2)
# Initialize the dp table
dp = [[0] * (len_s2 + 1) for _ in range(len_s1 + 1)]
# Set initial conditions
for i in range(len_s1 + 1):
dp[i][0] = i
for j in range(len_s2 + 1):
dp[0][j] = j
# Fill in the dp table
for i in range(1, len_s1 + 1):
for j in range(1, len_s2 + 1):
if s1[i - 1] == s2[j - 1]:
cost = 0
else:
cost = 1
dp[i][j] = min(
dp[i - 1][j] + 1, # Deletion
dp[i][j - 1] + 1, # Insertion
dp[i - 1][j - 1] + cost # Substitution
)
return dp[len_s1][len_s2]
# Example
s1 = "kitten"
s2 = "sitting"
distance = levenshtein_distance(s1, s2)
print(f'Levenshtein distance between "{s1}" and "{s2}": {distance}') # Output: 3
s1 = "intention"
s2 = "execution"
distance = levenshtein_distance(s1, s2)
print(f'Levenshtein distance between "{s1}" and "{s2}": {distance}') #Output: 5
Dynamic programming allows us to efficiently calculate the Levenshtein distance. This algorithm has various applications in areas such as string similarity comparison and spell checking.