k-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) is one of the simplest machine learning algorithms. It can be used for both classification and regression problems, and it performs well particularly on non-linear data.
Basic Concept
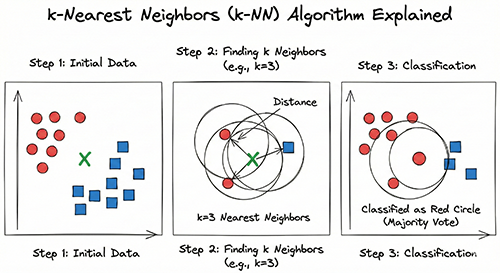
- Training Data: Prepare known input data with their correct labels (or values).
- Unknown Data: Prepare a new input data point that you want to classify.
- Distance Calculation: Calculate the distance between the unknown data point and each data point in the training set. (You can use various distance metrics like Euclidean distance, Manhattan distance, etc.)
- Neighbor Selection: Select the k nearest data points from the training set based on the calculated distances.
- Majority Vote (Classification) / Averaging (Regression):
- For Classification: Predict the label of the unknown data point as the most frequent label among the k nearest neighbors.
- For Regression: Predict the value of the unknown data point as the average value of the k nearest neighbors.
Example: Classifying Flower Types with KNN
Data:
| Flower Color | Petal Length | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Red | 5.0 | Morning Glory |
| Red | 4.8 | Morning Glory |
| White | 6.2 | Lily |
| White | 6.0 | Lily |
| Yellow | 7.1 | Rose |
| Yellow | 6.9 | Rose |
Unknown Data: Predict the type of a flower with Red color and Petal Length of 5.2.
Steps:
- Distance Calculation: Calculate the Euclidean distance between the unknown data point and each data point in the training set.
- (5.0-5.2)^2 + (0-0)^2 = 0.04
- (4.8-5.2)^2 + (0-0)^2 = 0.16
- (6.2-5.2)^2 + (0-0)^2 = 1.00
- (6.0-5.2)^2 + (0-0)^2 = 0.64
- (7.1-5.2)^2 + (0-0)^2 = 3.61
- (6.9-5.2)^2 + (0-0)^2 = 2.89
- Neighbor Selection: If k=3, the 3 nearest data points are:
- Red, 5.0, Morning Glory (distance: 0.04)
- Red, 4.8, Morning Glory (distance: 0.16)
- White, 6.2, Lily (distance: 1.00)
- Majority Vote: Among the k nearest neighbors, Morning Glory appears twice and Lily once. Therefore, we predict the type of the unknown data point as Morning Glory.
Python Code Example (using scikit-learn)
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
import numpy as np
# Training Data
X_train = np.array([[5.0, 0], [4.8, 0], [6.2, 0], [6.0, 0], [7.1, 0], [6.9, 0]]) # Flower color and petal length
y_train = np.array(['Morning Glory', 'Morning Glory', 'Lily', 'Lily', 'Rose', 'Rose']) # Type
# Unknown Data
X_test = np.array([[5.2, 0]]) # Flower color and petal length
# Create a KNN model (k=3)
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)
# Train the model
knn.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Predict the label of the unknown data point
prediction = knn.predict(X_test)
print("Prediction:", prediction[0]) # Output: Morning Glory
Advantages and Disadvantages of KNN
Advantages:
- Simple and easy to understand
- Can handle non-linear data
- Low training cost (only needs to store the training data)
Disadvantages:
- High computational cost (needs to calculate distances to all training data points for each unknown data point)
- Curse of dimensionality: Accuracy can decrease as the number of features increases.
- Sensitive to outliers.
KNN is a powerful machine learning algorithm that is simple yet effective. By selecting an appropriate value of k based on the characteristics and purpose of the data, it can achieve high prediction performance. However, for large datasets, other algorithms may be considered due to its computational cost.