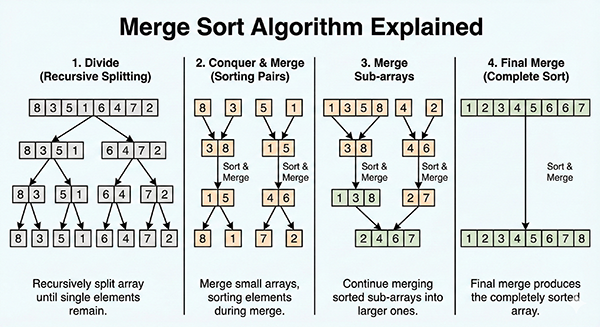
Merge sort is an efficient sorting algorithm based on the divide-and-conquer paradigm. It recursively divides a large array into smaller sub-arrays, sorts those sub-arrays, and then merges them back together to create the final sorted array.
Features:
- Stable Sort: Maintains the relative order of equal elements.
- Time Complexity: O(n log n) in best, average, and worst cases.
- Space Complexity: Requires O(n) additional memory (used for storing sub-arrays).
Algorithm Steps
- Divide: Recursively divide the array into halves until the sub-arrays have a size of 1 or 2 elements.
- Conquer: Consider sub-arrays with sizes of 1 or 2 to be already sorted.
- Merge: Merge the sorted sub-arrays to create new sorted arrays.
Example
Let’s look at the process of sorting the array [8, 3, 1, 7, 0, 10, 2] using merge sort.
- Divide:
[8, 3, 1, 7],[0, 10, 2][8, 3],[1, 7],[0, 10],[2][8],[3],[1],[7],[0],[10],[2]
- Conquer:
- Each sub-array has a size of 1, so they are considered sorted.
- Merge:
[3, 8],[1, 7],[0, 10],[2][1, 3, 7, 8],[0, 2, 10][0, 1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 10]
Python Code
def merge_sort(arr):
"""
Sorts an array using merge sort.
Args:
arr: The array to be sorted.
Returns:
A new sorted array.
"""
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr # Return the array as is if it has 1 or fewer elements
mid = len(arr) // 2 # Calculate the middle index of the array
left = arr[:mid] # Left sub-array
right = arr[mid:] # Right sub-array
# Recursively sort the sub-arrays
left = merge_sort(left)
right = merge_sort(right)
# Merge the sorted sub-arrays
return merge(left, right)
def merge(left, right):
"""
Merges two sorted arrays.
Args:
left: The sorted left array.
right: The sorted right array.
Returns:
A new merged and sorted array.
"""
result = []
i = 0
j = 0
while i < len(left) and j < len(right):
if left[i] <= right[j]:
result.append(left[i])
i += 1
else:
result.append(right[j])
j += 1
# Add any remaining elements from the sub-arrays
result += left[i:]
result += right[j:]
return result
# Example usage
arr = [8, 3, 1, 7, 0, 10, 2]
sorted_arr = merge_sort(arr)
print(f"Before sorting: {arr}")
print(f"After sorting: {sorted_arr}")
- Merge sort uses recursive calls, which can lead to stack overflow for very large arrays. Consider an iterative implementation in such cases.
- Merge sort is a stable sorting algorithm, meaning it preserves the relative order of equal elements. This can be important in certain applications.